
It's ranking in this criterion jumped from 7th to first. This was on the back of its extraordinary achievement in economic performance. In this year's ranking, Ireland made the most impressive overall improvement as it leapt from 11th place to second. Hard data accounts for two-thirds of the overall ranking results, whereas the survey data represents one-third. The institute explains that the results are based on a mixture of hard data - 164 competitiveness criteria selected as a result of comprehensive research using economic literature, international, national, and regional sources, plus feedback from the business community, government agencies, and academics - and 92 survey questions answered by 6,400 senior executives. The criteria are revised and updated regularly as new theories, research, and data become available and as the global economy evolves.
The World Competitiveness Ranking is based on 336 competitiveness criteria selected as a result of comprehensive research using economic literature, international, national, and regional sources, and feedback from the business community, government agencies, and academics. In India, it partners with the National Productivity Council.

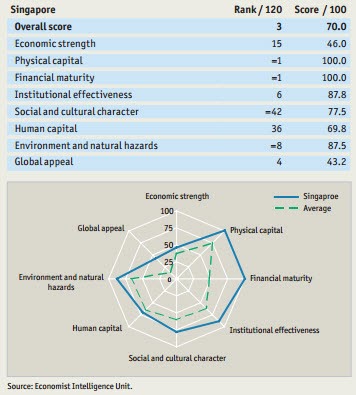
In Singapore, the institute works with the Ministry of Trade and Industry's economics division, and the Singapore Business Federation. The report is produced with the support of a network of 57 local partner institutes. It also "serves managers and policymakers alike and is an indicator of the quality of life in each country it assesses." It's not what China does yet and it's not what the US even does fully yet," said Professor Arturo Bris, Director of the WCC.Īccording to the institute, which is co-headquartered in Switzerland and Singapore, the ranking provides a "valuable tool for evaluating highly contrasting business environments, for supporting international investment decisions, and for assessing the impact of various public policies." "A country's ability to generate prosperity for its people is a key determiner of success. In addition to GDP and productivity, it looks into how enterprises cope with political, social and cultural factors.

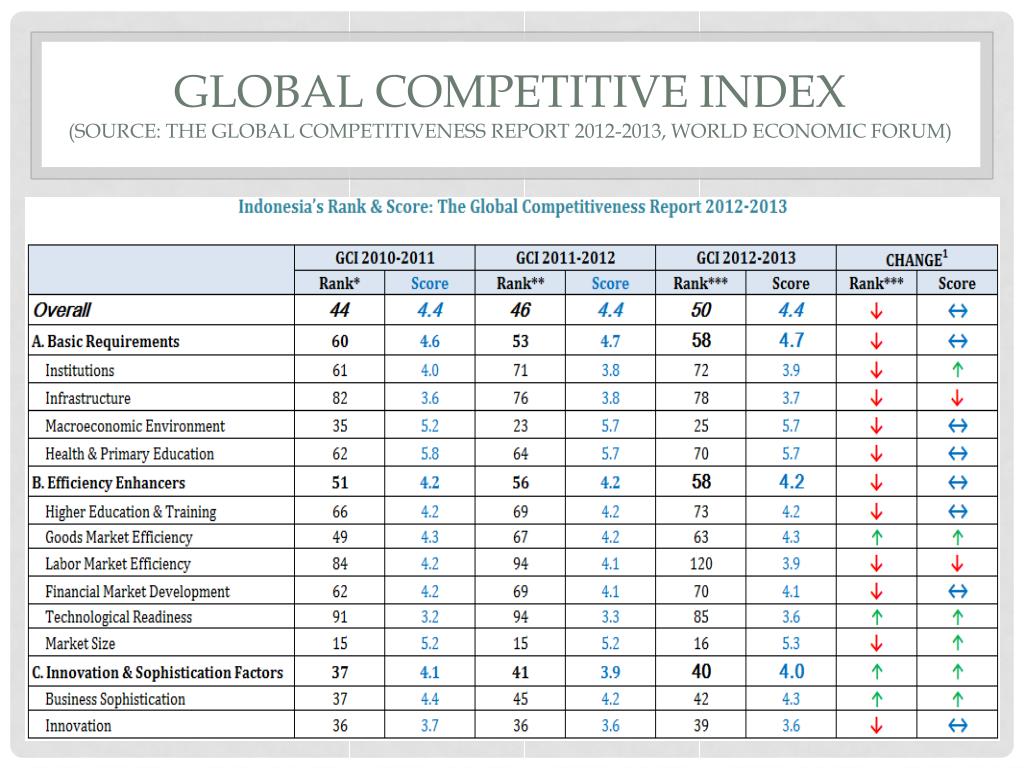
It analyses and ranks countries according to how they manage their competencies to achieve long-term value creation. The report uses a combination of surveys, statistical data and trends to benchmark the competitiveness of 64 countries around the world. First published in 1989, IMD World Competitiveness Yearbook (WCY), is a comprehensive annual report and worldwide reference point on the competitiveness of countries.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
